In the last post we looked at a magnetometer example this time we will look at the default accelerometer example
The LSM303 3D Accelerometers/Magnetometer Models are a system-in-package featuring a 3D digital linear acceleration sensor and a 3D digital magnetic sensor. These best-in-class eCompass devices enable superior PDR or unique use cases in emerging applications, including drones and personal navigation systems.
All full-scales available are fully selectable by the user. The device includes an I2C serial bus interface that supports standard and fast mode 100kHz and 400kHz.
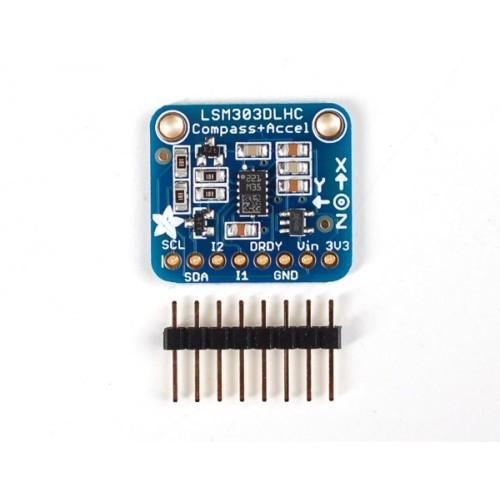
Here is a picture of the module I bought
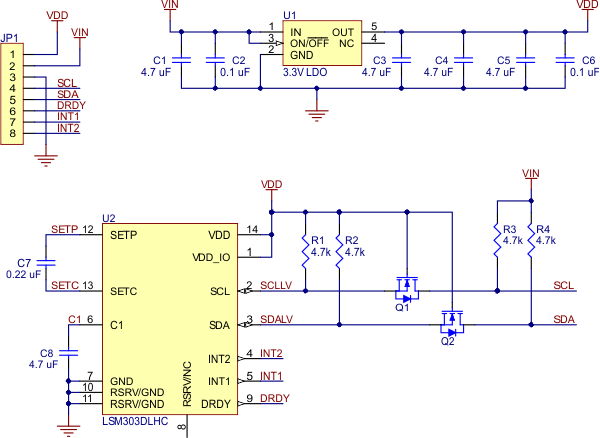
This is a schematic of a typical module such as the one above
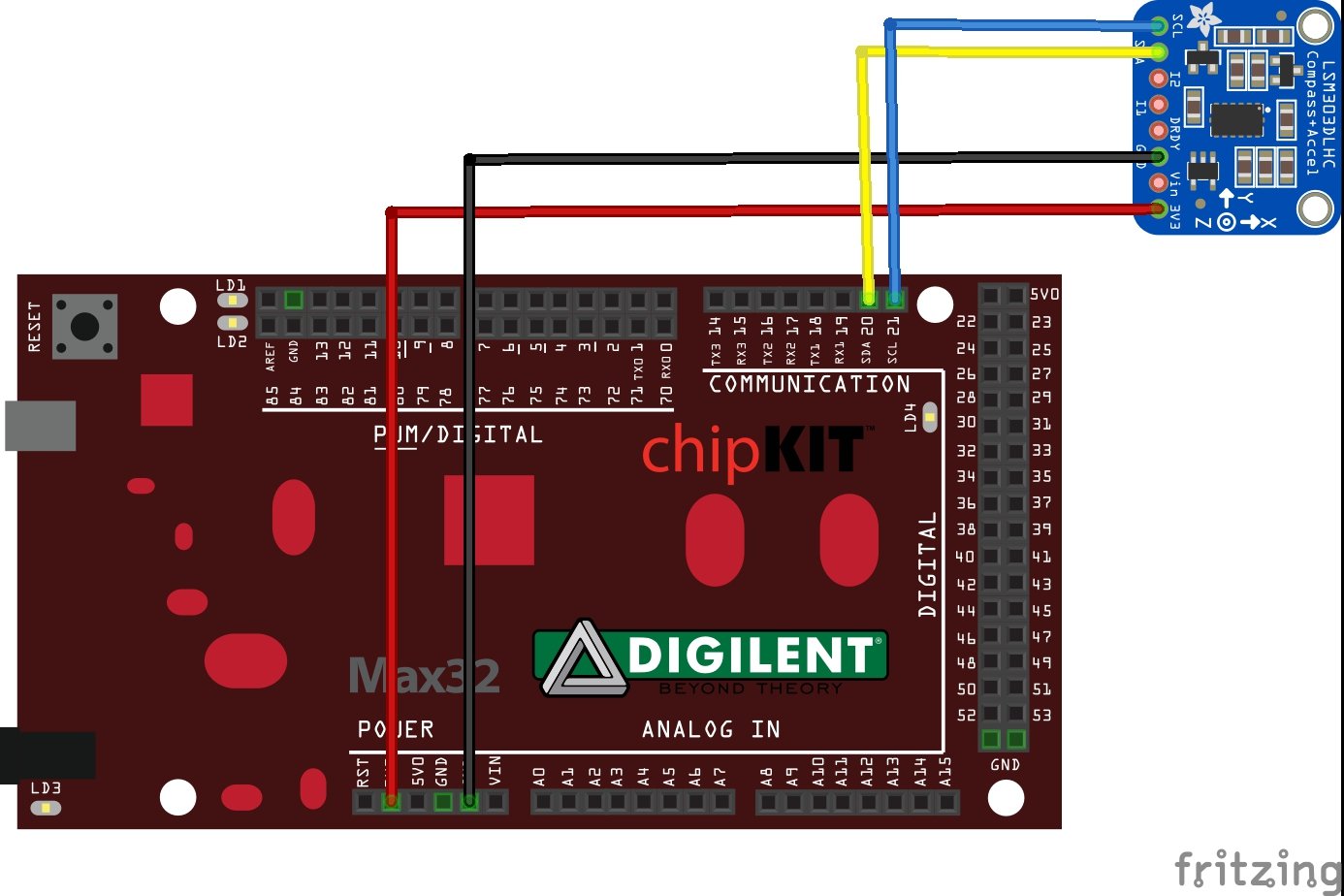
Now lets look at a layout showing how to connect the module to our Arduino
Schematic and layout
Quite a straightforward connection being an I2C device
Code
This requires the LSM303 Adafruit to be added to the Arduino IDE via the library manager
This is the default accelerometer example
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Adafruit_LSM303_U.h>
/* Assign a unique ID to this sensor at the same time */
Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified accel = Adafruit_LSM303_Accel_Unified(54321);
void displaySensorDetails(void)
{
sensor_t sensor;
accel.getSensor(&sensor);
Serial.println("------------------------------------");
Serial.print ("Sensor: ");
Serial.println(sensor.name);
Serial.print ("Driver Ver: ");
Serial.println(sensor.version);
Serial.print ("Unique ID: ");
Serial.println(sensor.sensor_id);
Serial.print ("Max Value: ");
Serial.print(sensor.max_value);
Serial.println(" m/s^2");
Serial.print ("Min Value: ");
Serial.print(sensor.min_value);
Serial.println(" m/s^2");
Serial.print ("Resolution: ");
Serial.print(sensor.resolution);
Serial.println(" m/s^2");
Serial.println("------------------------------------");
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
}
void setup(void)
{
#ifndef ESP8266
while (!Serial); // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
#endif
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Accelerometer Test");
Serial.println("");
/* Initialise the sensor */
if(!accel.begin())
{
/* There was a problem detecting the ADXL345 ... check your connections */
Serial.println("Ooops, no LSM303 detected ... Check your wiring!");
while(1);
}
/* Display some basic information on this sensor */
displaySensorDetails();
}
void loop(void)
{
/* Get a new sensor event */
sensors_event_t event;
accel.getEvent(&event);
/* Display the results (acceleration is measured in m/s^2) */
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(event.acceleration.x);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Y: ");
Serial.print(event.acceleration.y);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Z: ");
Serial.print(event.acceleration.z);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println("m/s^2 ");
/* Note: You can also get the raw (non unified values) for */
/* the last data sample as follows. The .getEvent call populates */
/* the raw values used below. */
Serial.print("X Raw: ");
Serial.print(accel.raw.x);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Y Raw: ");
Serial.print(accel.raw.y);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print("Z Raw: ");
Serial.print(accel.raw.z);
Serial.println("");
/* Delay before the next sample */
delay(500);
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Open the Serial Monitor window and you should see something like this
Accelerometer Test
————————————
Sensor: LSM303
Driver Ver: 1
Unique ID: 54321
Max Value: 0.00 m/s^2
Min Value: 0.00 m/s^2
Resolution: 0.00 m/s^2
————————————
X: 6.00 Y: 9.38 Z: -2.20 m/s^2
X Raw: 612 Y Raw: 956 Z Raw: -224
X: 1.69 Y: 3.57 Z: -9.45 m/s^2
X Raw: 172 Y Raw: 364 Z Raw: -964
X: 5.26 Y: -0.04 Z: 2.82 m/s^2
X Raw: 536 Y Raw: -4 Z Raw: 288
X: 1.18 Y: 14.83 Z: -17.26 m/s^2
X Raw: 120 Y Raw: 1512 Z Raw: -1760
X: -0.71 Y: -0.75 Z: -5.73 m/s^2
X Raw: -72 Y Raw: -76 Z Raw: -584
Links